-
Ipamorelin 10mg $80.00
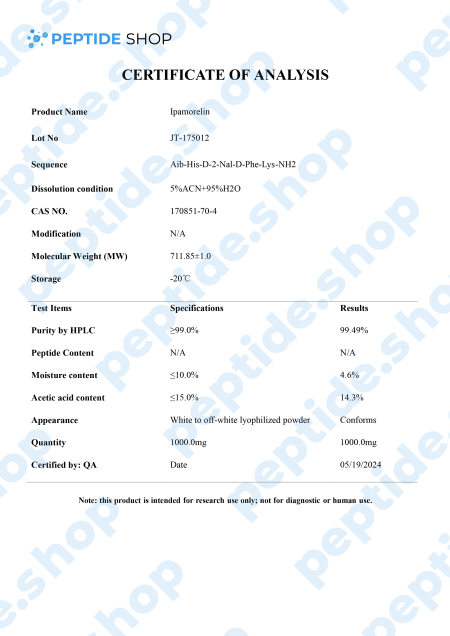
Ipamorelin is a pentapeptide that showed a significant growth hormone secretion potential both in vitro and in vivo studies. In vivo studies, it showed a similar potency and effectiveness as GHRP-6 (a synthetic growth hormone-releasing hexapeptide) as it stimulates GH release via the GHRP receptors.
What’s interesting about ipamorelin is that it did not raise ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) nor cortisol level significantly; something we’ve seen happening with GHRP-6 and GHRP-2. So, we can conclude that ipamorelin is the first GHRP-receptor agonist with GH release selectivity similar to GHRH. This is why ipamorelin is an interesting candidate for further testing.
In addition to stimulating GH secretion, this peptide has seen some interesting use in the treatment of postoperative ileus (POI), a condition characterized by transient loss of gastrointestinal motility following abdominal surgery.
The exact mechanism behind POI is a complex one, involving many different bodily structures; in addition, condition is often worsen due to the opioid drugs used for patient pain management.
In rodent studies, ipamorelin was found to selectively stimulate ghrelin (hormone produced by our stomach, affecting food intake, deposition and growth hormone release) without raising cortisol or adrenocorticotropic hormone levels. These effects were shown in both lower GI tract as well as the upper, making this peptide a viable candidate for potential POI treatment.
References:
Raun K, Hansen BS, Johansen NL, Thøgersen H, Madsen K, Ankersen M, Andersen PH. Ipamorelin, the first selective growth hormone secretagogue. Eur J Endocrinol. 1998 Nov;139(5):552-61. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1390552. PMID: 9849822.
Greenwood-Van Meerveld B, Tyler K, Mohammadi E, Pietra C. Efficacy of ipamorelin, a ghrelin mimetic, on gastric dysmotility in a rodent model of postoperative ileus. J Exp Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 19;4:149-55. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S35396. PMID: 27186127; PMCID: PMC4863553.
-
TB-500 10mg $80.00 – $140.00
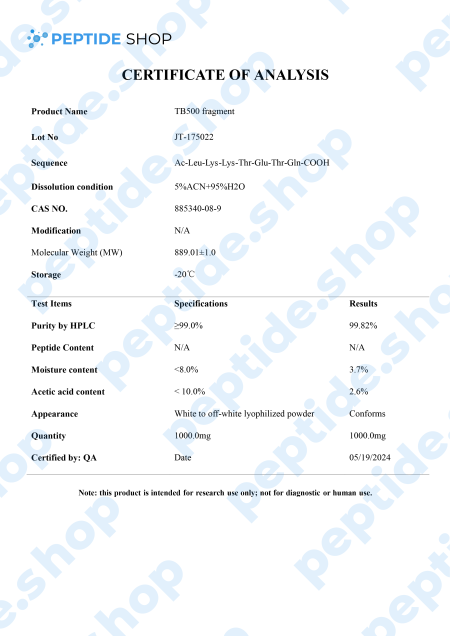
TB-500 is a 43 amino acid long synthetic peptide, analogue of thymosin beta-4. Thymosin beta-4 is a widely distributed peptide, and present in virtually all mammalian cells, which plays a pivotal role in many different processes in the body – it increases angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), proliferation, inhibits apoptosis (cell death) and inflammation.
Numerous animal clinical trials also showed that thymosin beta-4 can be used to indicate myocardial, liver and renal problems.
Angiogenesis:
Thymosin beta-4 promotes angiogenesis, triggers cell proliferation and migration, as well as the formation of capillary-like structures in cells. It also triggers blood perfusion (local fluid flow) by increasing capillary density.
Apoptosis:
Thymosin beta-4 inhibits apoptosis by inhibiting the transforming growth factor pathway. It also prevents nucleus pulposus (spinal disk providing shock absorption during movement) cell apoptosis and slows down cellular aging.
Inflammation:
In mouse models Tβ4 significantly dropped the number of inflammatory cells in the brains of the treated animals. It also prevented the production of proinflammatory cytokines and effectively blocked the increase of ethanol-induced inflammatory factors.
Heart Health:
Clinical data showed that thymosin beta-4 has a positive effect on both acute phase (immediately following the injury) where it preserves the ischemic myocardium, as well as in the chronic phase, in which it activates the growth of vascular cells.
After observing Tβ4’s benefits in animal models, it’s not surprising TB-500 gained so much popularity recently, since it acts as Tβ4’s synthetic analogue. Numerous clinical studies (in animal models) showed TB-500 as a potent way to improve blood vessel growth and fluid flow, accelerate wound healing, reduce oxidative stress and bind protein.
Of course, more research is needed to determine the full effects of this peptide, its safety and effectiveness in human test subjects.
Reference:
Xing Y, Ye Y, Zuo H, Li Y. Progress on the Function and Application of Thymosin β4. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 21;12:767785. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.767785. PMID: 34992578; PMCID: PMC8724243.

Collection

the best price

& Winter 2018
 Anti Aging
Anti Aging Hair Growth
Hair Growth Muscle Growth
Muscle Growth Peptide Blends
Peptide Blends Peptide Supplies
Peptide Supplies Peptides
Peptides Skin
Skin Testosterone
Testosterone Weight Loss
Weight Loss