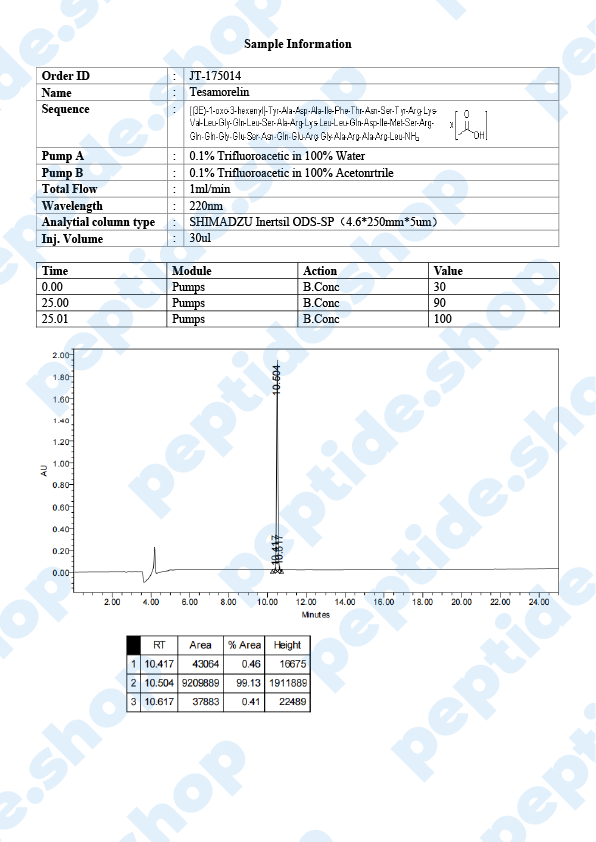
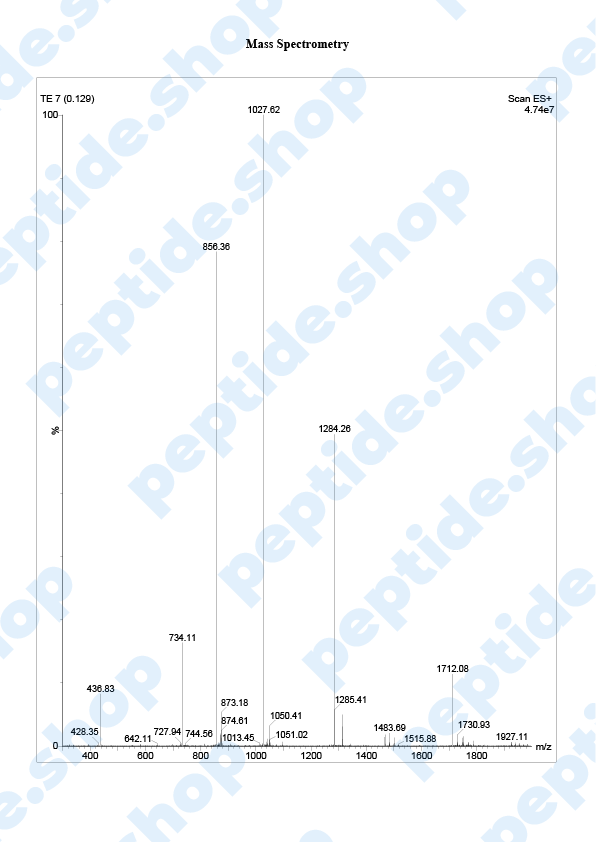
Tesamorelin
Tesamorelin is a 44 amino acid long, synthetic growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) analogue. It was primarily developed and used to treat visceral fat buildup in HIV positive patients suffering from lipodystrophy (a condition characterized by abnormal fat distribution).
Tesamorelin peptide activates GHRH receptors in the pituitary gland, resulting in growth hormone synthesis and release. This GH release further stimulates the production of Ilike growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which is naturally low in obese and diabetic patients.
The good thing about tesamorelin is that it was approved in the US back in 2010 for the treatment of abdominal fat in HIV positive patients as a part of the antiviral therapy-related lipodystrophy. It has also been evaluated as a potential therapy of insulin resistance, nonalcoholic fatty liver and, of course, obesity. These clinical studies are still ongoing and we’ll need more information to confirm its effectiveness.
The usual tesamorelin dosage for patients is 2mg given in the form of a subcutaneous injection, once a week. As for the side effects, patients did not report that many, but from the ones we have documented, most common are:
- Application site irritation
- Itching
- Peripheral edema
- Mild nausea
- Redness
More importantly, tirzepatide therapy was not associated with hepatotoxicity and is very unlikely to cause any clinically apparent liver injuries.
Reference:
$75.00 – $130.00
| Quantity: | 5mg, 10mg |
|---|---|
| Unit: | 1 vial |
| Contents: | Tesamorelin |
| Form/Appearance: | Lyophilized/Powder |
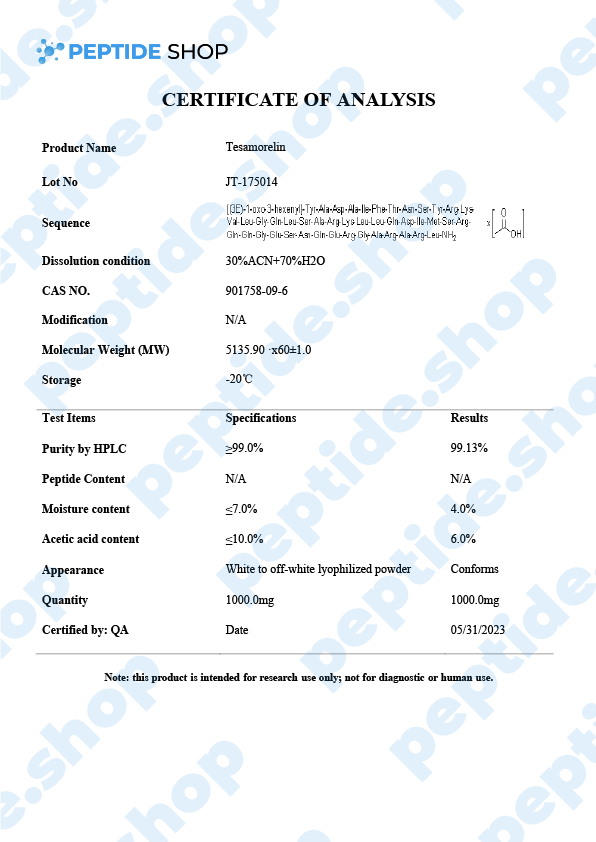
| Peptide Purity: | 99% |
| Sequence: | Trans-3-Hexenoyl-Tyr-Ala-Asp-Ala-Ile-Phe-Thr-Asn-Ser-Tyr-Arg-Lys-Val-Leu-Gly-Gln-Leu-Ser-Ala-Arg-Lys-Leu-Leu-Gln-Asp-Ile-Met-Ser-Arg-Gln-Gln-Gly-Glu-Ser-Asn-Gln-Glu-Arg-Gly-Ala-Arg-Ala-Arg-Leu-NH2 |
| Molecular Mass: | 5135.8 g/mol |
| Solubility: | Sterile / Bacteriostatic water |
| Synonyms: | TH9507 |
Based on 0 reviews
|
|
|
0% |
|
|
|
0% |
|
|
|
0% |
|
|
|
0% |
|
|
|
0% |
FAQs
Related Products
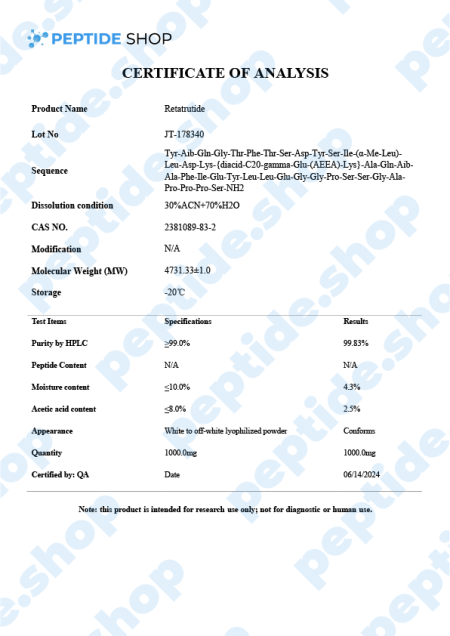
Retatrutide is one of the latest incretin mimetic drugs being tested for their weight reduction properties. Researchers use incretin mimetic agents as they work to mimic incretin hormones (gut peptides that get secreted after we eat) to allow for a better insulin secretion and hyperglycaemic control.
Even though there are numerous weight reduction agents being prescribed and used, FDA-recognized “treatment” for nonsyndromic obesity are:
- Orlistat
- Phentermine-topiramate
- Naltrexone‐bupropion
- Liraglutide and
- Semaglutide
With the exception of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (such as semaglutide), most weight reduction agents come with a specific set of side effects such as nausea, gastrointestinal distress, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, or a general weight decrease that does not cross the 15% mark. Some of these medications even come with a warning against using them if a patient is suffering from a kidney, heart, thyroid or any related problems.
This is why scientists are turning more and more to retatrutide, because this incretin mimetic decreases appetite, promotes the feeling of fullness and slows down the process of gastric emptying, but does all that while presenting with minimal side effects and increased weight loss effectiveness, compared to liraglutide or semaglutide.
Retatrutide Mechanism of Action
Retatrutide exerts a powerful glucagon-receptor agonistic effect. When we compare it to human glucagon and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), it exhibits:
- Reduced potency on the GCGR (human glucagon receptor) and GLP-1R (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor)
- Enhanced potency at the human GIPR (gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor)
When talking about in vitro experiments, retatrutide demonstrated similar efficacy in evoking glucose production within hepatocytes and inducing lipolysis. Also, retatrutide showed a favorable half-life of 6 days, enabling it a weekly dosage regimen (should the drug get FDA approved).
Another double-blind study conducted in the US on obese patients showed promising results. 338 adults in total were involved, split into 6 cohorts (depending on the weekly dosage), up against a placebo group. Retatritude group experienced the following results:
- 1mg group – after 24 weeks this group experienced weight loss of 7.2%, and after 48 weeks a total loss of 8.7%
- 4mg group (commencing with 2mg) – after 24 weeks this group experienced a weight loss of 11.8%, and after 48 weeks a total loss of 16.3%
- 4mg group (commencing with 4mg) – after 24 weeks this group experienced a weight loss of 13.9%, and after 48 weeks a total loss of 17.8%
- 8mg group (commencing with 2mg) – after 24 weeks this group experienced a weight loss of 16.7%, and after 48 weeks a total loss of 21.7%
- 8mg group (commencing with 4mg) – after 24 weeks this group experienced a weight loss of 17.9%, and after 48 weeks a total loss of 23.9%
- 12mg group (commencing with 2mg) – after 24 weeks this group experienced a weight loss of 17.5%, and after 48 weeks a total loss of 24.2%
In contrast, the placebo group only experienced a 1.6% weight loss after 24 weeks and 2.1% after 48. Findings also showed that adverse effects related to retratitude treatment (such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and constipation), were mild and depended on the dosage.
In conclusion, this peptide showed promising results in addressing obesity in both in vitro and human test subject studies. However, test samples were relatively small, and we still need more research and clinical trials to show the effectiveness of retratutide as an effective, long-term way of managing weight.
Reference:
Naeem M, Imran L, Banatwala UESS. Unleashing the power of retatrutide: A possible triumph over obesity and overweight: A correspondence. Health Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 5;7(2):e1864. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1864. PMID: 38323122; PMCID: PMC10844714.
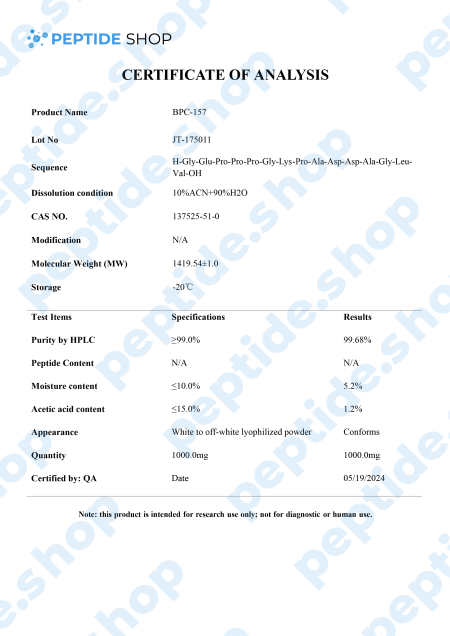
BPC-157 is a native gastric pentadecapeptide (composed of 15 amino acids), derivative of body protection compound (BPC). Being a gastric peptide allows for good oral availability and remaining stable for more than 24 hours in human gastric juice. Furthermore, there is no need for a carrier which makes this peptide unique, as compared to others that depend on it.
Clinical studies showed that BPC-157 is highly effective in both treatment and prophylaxis of various gastrointestinal lesions. This effectiveness spans to cover both acute and chronic gastric conditions, intravenous, ingastric, and even as a topical agent for deep skin burns and lesions.
Surprisingly, BPC-157 has also shown a beneficial effect on:
- Brain lesions – in one of the most recent studies researchers concluded that BPC-157 expressed a direct therapeutic effect in rat test subjects following a stroke. This peptide not only delayed neural damage, but also promoted full functional recovery.
- Behavioral disorders – medical research showed that BPC-157 counteracted catalepsy (a state of a trance or a seizure) in rat models. This research indicated a connection between BPC-157 and dopamine as well as glutamate and nitric oxide system (vital in schizophrenia therapy).
- Spinal cord injuries – A particularly interesting study showed that BPC-157 administration to rats with spinal cord injuries resulted in improvements mere 10 minutes after the initial dosage. On the contrary, untreated rats did not fully recover days, weeks, months and, in some rare cases, years following the injury.
In conclusion, we saw BPC-157 application results in a myriad of beneficial effects in various different systems within the body. Of course, many of these studies were performed on animal test subjects and we’re going to need additional ones to clarify its effect in humans and the full extent of its therapeutic potential.
References:
Vukojevic J, Milavić M, Perović D, Ilić S, Čilić AZ, Đuran N, Štrbe S, Zoričić Z, Filipčić I, Brečić P, Seiverth S, Sikirić P. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and the central nervous system. Neural Regen Res. 2022 Mar;17(3):482-487. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.320969. PMID: 34380875; PMCID: PMC8504390.
Sikiric P, Hahm KB, Blagaic AB, Tvrdeic A, Pavlov KH, Petrovic A, Kokot A, Gojkovic S, Krezic I, Drmic D, Rucman R, Seiwerth S. Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157, Robert’s Stomach Cytoprotection/Adaptive Cytoprotection/Organoprotection, and Selye’s Stress Coping Response: Progress, Achievements, and the Future. Gut Liver. 2020 Mar 15;14(2):153-167. doi: 10.5009/gnl18490. PMID: 31158953; PMCID: PMC7096228.
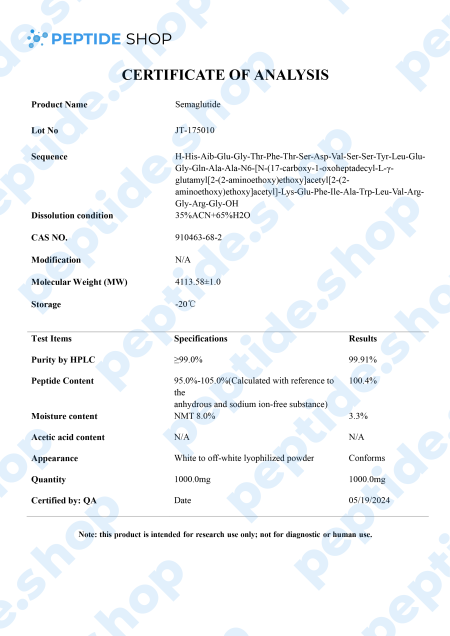
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist.It is one of the two primary hormones that may enhance incretin activity in rodent models, along with GIP.
GLP-1 is one of the major incretin (gut peptide secreted after nutrient intake) hormones in humans. It plays a pivotal role in many different mechanisms within the body:
- Insulin secretion
- Inhibits glucagon release (glucagon is secreted as a response in blood sugar drop)
- Suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis (glycogen is the primary carbohydrate stored in the liver)
- Delays gastric emptying
- Reduces appetite and energy intake
When talking about obese diabetic 2 type patients, GLP-1 assumes a special status in their treatment as it lowers HbA1c levels along with body weight, but without the risk of hypoglycemia.
However, the biggest problem with GLP-1 is its short half-live (of only 1 to 2 minutes) and this is why researchers turner to various other GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as liraglutide, dulaglutide and, of course, semaglutide. Another thing researchers hope to achieve by turning to GLP-1 agonists, such as semaglutide, is to develop an effective diabetes management drug which needs less frequent dosing.
Murine models suggested that semaglutide’s GLP-1 receptor activation affects insulin secretion, blood sugar homeostasis and beta cell protection. Further, in vitro studies showed its potential to also affect glucagon secretion. This insulin glucagon mechanics is what’s used to balance our pancreatic function and regulate metabolism.
References:
- Mahapatra MK, Karuppasamy M, Sahoo BM. Semaglutide, a glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonist with cardiovascular benefits for management of type 2 diabetes. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022 Jun;23(3):521-539. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09699-1. Epub 2022 Jan 7. PMID: 34993760; PMCID: PMC8736331.
- Meier JJ. GLP-1 receptor agonists for individualized treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Dec;8(12):728-42. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2012.140. Epub 2012 Sep 4. PMID: 22945360.
500 in stock
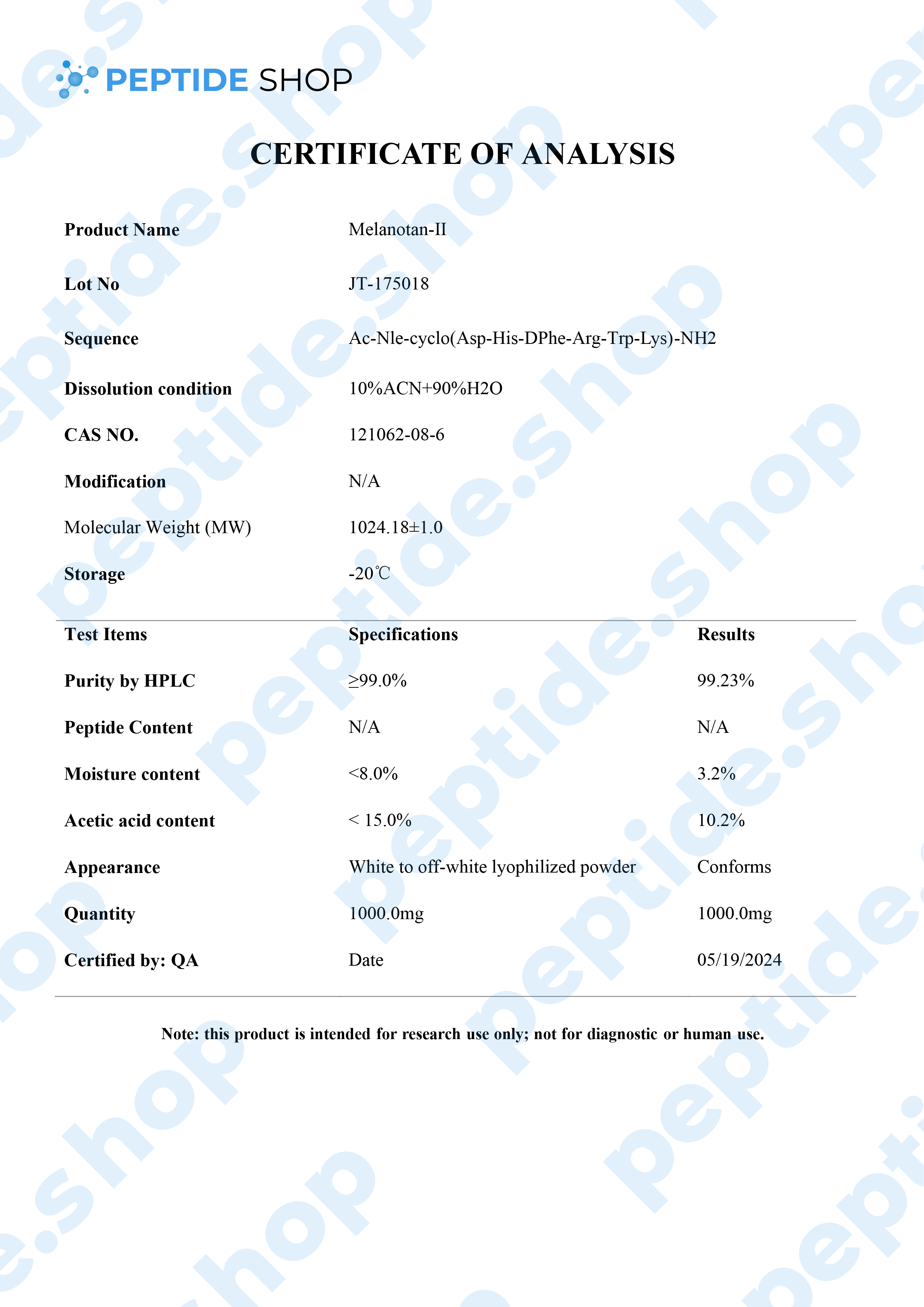
Melanotan 2 is a synthetic version of human alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone and acts as a non selective melanocortin-receptor agonist. It was mainly developed as a sunless tanning option, but some clinical studies showed it also causes spontaneous penile erections, as well as general sexual stimulation.
Some of the other “side effects” researchers noticed were reduction in compulsive behavior, reduced glucagon production, hunger suppression and even some limited addiction control.
Melanotan 2 Effects On Autism
There is some additional recent clinical research suggesting there might be a link between Mealnotan 2 and autism. Of course, melanotan treatment cannot reverse autism, sadly, but it may act on some aspects of this disorder and make it more manageable.
In mouse model studies researchers recorded that MT2 stimulated oxytocin release, which had the potential to reduce (in some cases counteract) common ASD behaviors – behaviors that include:
- Hand clapping
- Bouncing on toes
- Body rocking
- Holding body parts in unusual positions
- Repeating vocalizations etc.
Hunger and satiety signals are controlled by serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and a number of other systems within our body. When talking about weight loss and appetite modulation, there are agents that do it through pure central nervous system pathways, and those that target peripheral signals (that travel to the central nervous system).
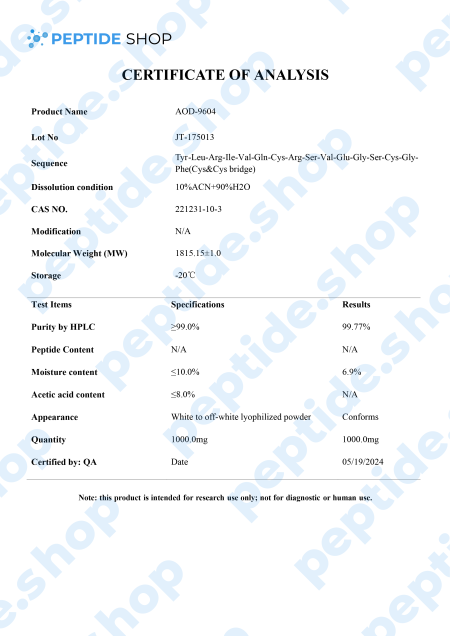
This is why we have so many different weight loss options, since medication is based on substances affecting different pathways, signals and weight management systems. One such drug, aimed at improving adipose tissue function and fatty acid metabolism is AOD9604.
AOD9604 is a modified form of human growth hormone fragment 176-191, developed to stimulate prolipid mobilizing and lipid oxidation (during which fatty acids decompose into carbonyl compounds, unsaturated aldehydes, ketones and other substances).
Even though AOD9604 has not yet been deemed FDA-approved,a number of studies showed its administration led to a significant weight loss and improvements in glucose tolerance (in both animal and early stage human studies).
Another such study done on 300 obese individuals in Australia showed that AOD9064 administration more than tripled weight loss in test subjects, compared to those on a placebo drug. Furthermore, this study proved that long-term treatment is not likely to cause resistance to AOD9064 based medication, making it a perfect candidate for future weight loss medication and treatment.
So far, animal and human studies both showed AOD9064’s effectiveness in helping test subjects lose weight, improve glucose tolerance, while presenting with minimal side effects. Further research studies are needed before including it into an FDA-approved treatment procedure, but the initial findings show a great potential.
Reference:
Michael D. Jensen. Potential Role of New Therapies in Modifying Cardiovascular Risk in Overweight Patients with Metabolic Risk Factors. 06 September 2012
Growth hormone replacement therapy has long been accepted as one of the most effective ways of treating GH deficiency and related conditions. This therapy uses recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) and, despite its longstanding usage record, it has been surrounded by controversy. Even though, in the short term, this therapy is very effective, when it comes to long term effects, issues start to arise:
- Long term improper dosage can lead to some severe side effects
- This therapy may affect normal physiology after prolonged application
- Some federal regulations might interfere with the therapy
- There’s even some concerns that this therapy may awaken latent cancers and cause metabolic disorders
There is one more major problem with dosage because the body can’t properly modulate tissue exposure to rhGH. Meaning, the practitioner uses their “best guess” to access the appropriate dosage.
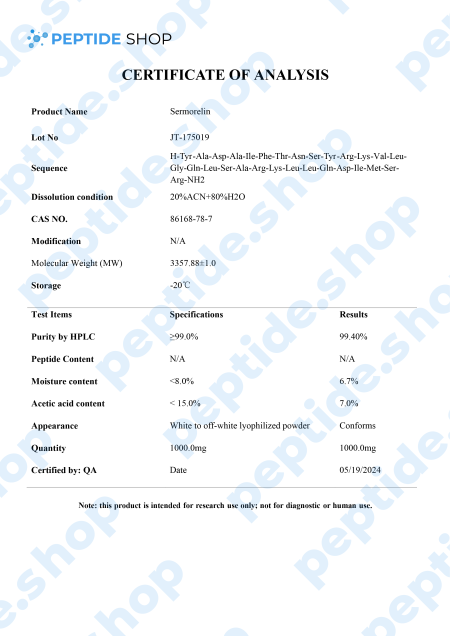
This is why researchers are looking for alternative ways to stimulate GH production by targeting GH secretagogues and promoting pituitary gland health. One such molecule is sermorelin, a GHRH analog that impacts the hypothalamic-pituitary-pituitary-somatotropic axis.
It’s used for both treatment and diagnosis of GH deficiency as research studies showed sermorelin promoted change in GH levels similar to those observed with endogenous GHRH. It also stimulates FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone), which implies a potential role in the treatment of hypogonadism.
Though we need larger, longitudinal studies, sermorelin proved as a promising GH and IGF-1 stimulator and diagnostic agent.
Reference:
Walker RF. Sermorelin: a better approach to management of adult-onset growth hormone insufficiency? Clin Interv Aging. 2006;1(4):307-8. doi: 10.2147/ciia.2006.1.4.307. PMID: 18046908; PMCID: PMC2699646.
Sinha DK, Balasubramanian A, Tatem AJ, Rivera-Mirabal J, Yu J, Kovac J, Pastuszak AW, Lipshultz LI. Beyond the androgen receptor: the role of growth hormone secretagogues in the modern management of body composition in hypogonadal males. Transl Androl Urol. 2020 Mar;9(Suppl 2):S149-S159. doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.11.30. PMID: 32257855; PMCID: PMC7108996.
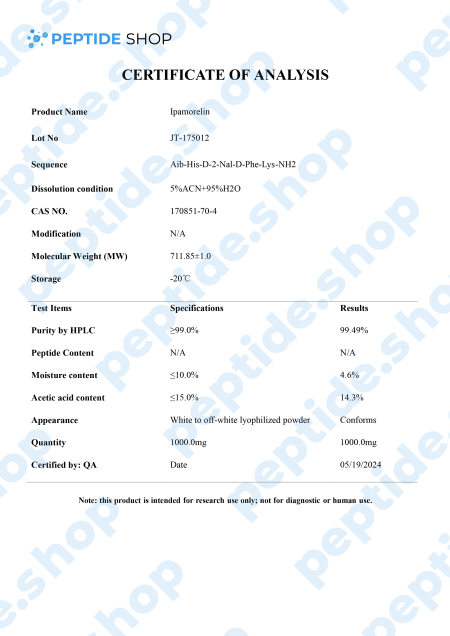
Ipamorelin is a pentapeptide that showed a significant growth hormone secretion potential both in vitro and in vivo studies. In vivo studies, it showed a similar potency and effectiveness as GHRP-6 (a synthetic growth hormone-releasing hexapeptide) as it stimulates GH release via the GHRP receptors.
What’s interesting about ipamorelin is that it did not raise ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) nor cortisol level significantly; something we’ve seen happening with GHRP-6 and GHRP-2. So, we can conclude that ipamorelin is the first GHRP-receptor agonist with GH release selectivity similar to GHRH. This is why ipamorelin is an interesting candidate for further testing.
In addition to stimulating GH secretion, this peptide has seen some interesting use in the treatment of postoperative ileus (POI), a condition characterized by transient loss of gastrointestinal motility following abdominal surgery.
The exact mechanism behind POI is a complex one, involving many different bodily structures; in addition, condition is often worsen due to the opioid drugs used for patient pain management.
In rodent studies, ipamorelin was found to selectively stimulate ghrelin (hormone produced by our stomach, affecting food intake, deposition and growth hormone release) without raising cortisol or adrenocorticotropic hormone levels. These effects were shown in both lower GI tract as well as the upper, making this peptide a viable candidate for potential POI treatment.
References:
Raun K, Hansen BS, Johansen NL, Thøgersen H, Madsen K, Ankersen M, Andersen PH. Ipamorelin, the first selective growth hormone secretagogue. Eur J Endocrinol. 1998 Nov;139(5):552-61. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1390552. PMID: 9849822.
Greenwood-Van Meerveld B, Tyler K, Mohammadi E, Pietra C. Efficacy of ipamorelin, a ghrelin mimetic, on gastric dysmotility in a rodent model of postoperative ileus. J Exp Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 19;4:149-55. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S35396. PMID: 27186127; PMCID: PMC4863553.
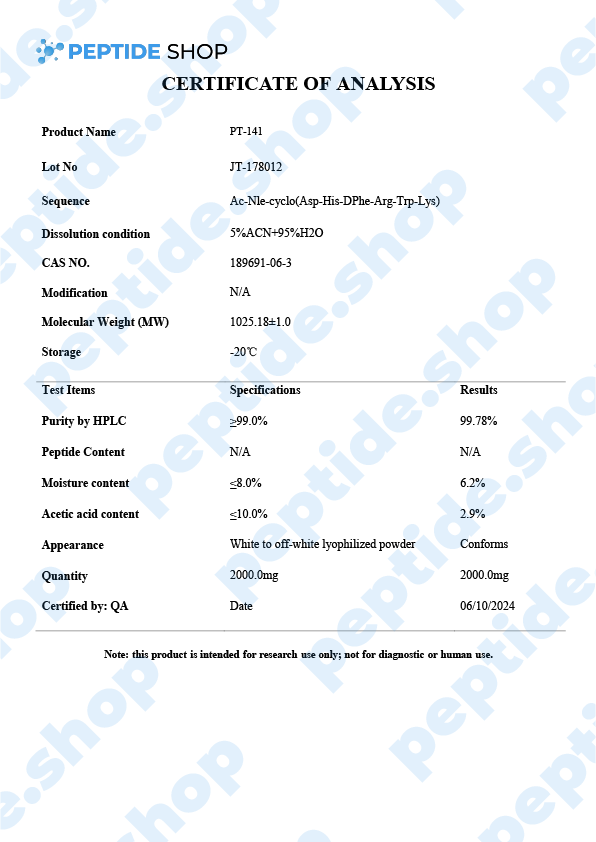
Also called Bremelanotide, PT-141 is a synthetic melanocortin receptor agonist that promotes dopamine release. Since it has such a high affinity for MC4R (Melanocortin 4 Receptor), in the presynaptic neurons of the hypothalamus, it has been approved as a treatment for HSDD (hypoactive sexual desire disorder) in premenopausal women. Under the brand name Vyleesi, Bremelanotide is the first and only FDA-approved way of HSDD treatment.
Sexual Dysfunctions
As we already said, PT-141 is an effective treatment for HSDD in premenopausal women but it’s important to note it should not be used as a treatment in women who already went through menopause or as a way of boosting sexual performance in men. These have not yet been fully tested.
We’ve seen the effectiveness of PT-141 (Bremelanotide) demonstrated in numerous studies. One such study followed female test subjects over the course of 52 weeks where the treated group received a 1.75mg dose right before anticipated sexual intercourse. All participants showed higher scores on general arousal, desire and orgasm, as compared to the placebo group. Also, no major side effects were linked to PT-141 application – the “most severe” ones were nausea, flushing and headache, which only occurred in around 10% of the participants.
Interestingly enough, scientists are still unsure about the Bremelanotide’s exact mechanism of action and how it leads to increased sexual desire in female patients. All we know is that it’s a potent alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone, binding predominantly to the receptors MC4R and MC1R, and, to a certain extent, to MC1R-MC5R.
PT-141 And Erectile Dysfunction
At the beginning of the article we said that PT-141 (bremelanotide) should not be used to increase sexual desire in men… but this is not entirely true as there is some emerging evidence that this peptide does affect male sexual performance.
Currently, there are a number of effective ED treatment options available. One of the most fail-proof and common ones, incidentally the most invasive one, is an intracavernosal injection – where an injection is applied directly to corpus cavernosum (spongy tissue that runs through the shaft of the penis).
Naturally, researchers are on the lookout for a new, less invasive treatment option and are testing PT-141 as such. Though research is still in its early stages, results showed significant increases in both duration and the erection quality in both “regular” men, as well as those known to be taking viagra.
We still need more research to confirm all these findings and determine the safety and efficacy of using PT-14 as a reliable ED treatment option, but clinical studies suggest we are heading in this direction.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/bremelanotide
Cagrisema 10mg is one of the latest PeptideShop’s peptide blends, which combines cagrilintide and semaglutide. Each vial contains a combination of lyophilized cagrilintide and semaglutide, 5mg each, tested for purity and strength, and suitable for lab experiments and chemical trials.
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist. GLP-1 is one of the main gut peptide hormones in humans, which plays a role in many different mechanisms within the body from insulin secretion, glucagon release, gastric emptying, appetite and energy intake.
And cagrilintdide is an amylin analogue co-secreted with insulin, which plays a role in glycemic control and gastric emptying.
Researchers hypothesize that this combination profoundly influences receptor changes in the brain, insulin secretion, appetite regulation and glucagon secretion.
Though this combination has not yet been fully tested, we have data from a study on the effects of Cagrisema on patients with type 2 diabetes.This was a 32-week, double-blind study across 17 sites in the USA, conducted on 92 individuals in total.
Final results showed that cagrisema resulted in clinically relevant improvements in glycaemic control (significant change in HbA1c) and, more importantly, a greater weight loss versus semaglutide as well as cagrilintide.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(23)01163-7/abstract
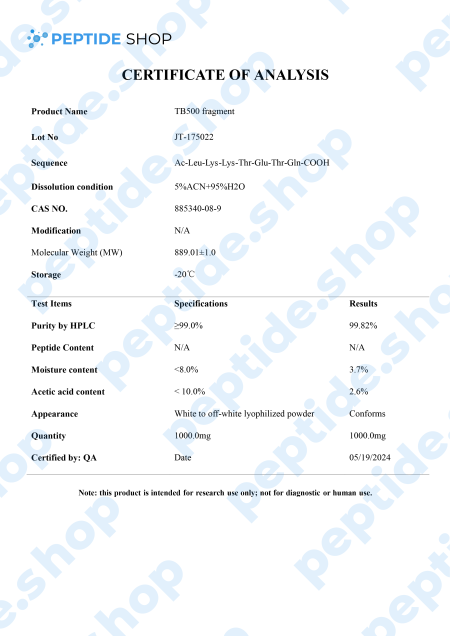
TB-500 is a 43 amino acid long synthetic peptide, analogue of thymosin beta-4. Thymosin beta-4 is a widely distributed peptide, and present in virtually all mammalian cells, which plays a pivotal role in many different processes in the body – it increases angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), proliferation, inhibits apoptosis (cell death) and inflammation.
Numerous animal clinical trials also showed that thymosin beta-4 can be used to indicate myocardial, liver and renal problems.
Angiogenesis:
Thymosin beta-4 promotes angiogenesis, triggers cell proliferation and migration, as well as the formation of capillary-like structures in cells. It also triggers blood perfusion (local fluid flow) by increasing capillary density.
Apoptosis:
Thymosin beta-4 inhibits apoptosis by inhibiting the transforming growth factor pathway. It also prevents nucleus pulposus (spinal disk providing shock absorption during movement) cell apoptosis and slows down cellular aging.
Inflammation:
In mouse models Tβ4 significantly dropped the number of inflammatory cells in the brains of the treated animals. It also prevented the production of proinflammatory cytokines and effectively blocked the increase of ethanol-induced inflammatory factors.
Heart Health:
Clinical data showed that thymosin beta-4 has a positive effect on both acute phase (immediately following the injury) where it preserves the ischemic myocardium, as well as in the chronic phase, in which it activates the growth of vascular cells.
After observing Tβ4’s benefits in animal models, it’s not surprising TB-500 gained so much popularity recently, since it acts as Tβ4’s synthetic analogue. Numerous clinical studies (in animal models) showed TB-500 as a potent way to improve blood vessel growth and fluid flow, accelerate wound healing, reduce oxidative stress and bind protein.
Of course, more research is needed to determine the full effects of this peptide, its safety and effectiveness in human test subjects.
Reference:
Xing Y, Ye Y, Zuo H, Li Y. Progress on the Function and Application of Thymosin β4. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 21;12:767785. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.767785. PMID: 34992578; PMCID: PMC8724243.
Obesity’s become a global pandemic, currently affecting one third of the entire population, and this is why we can look at it as a chronic disease that requires appropriate treatment.
When talking about obesity, amylin hormone is of great importance as it gets secreted along with insulin and acts as food intake inhibitor, delaying gastric emptying and suppresses post-prandial glucagon responses to meals.
For this reason, there is a tendency to include amylin management in newly developed medication.
And one such compound is cagrilintide – lipidated long-acting amylin analogue.
Though it still hadn’t been thoroughly tested on humans, numerous rat studies showed incredible potential. One such in vitro study involving rats set out to compare cagrilintide’s effectiveness against pramlintide (an FDA-approved diabetes 1/2 medication).
The study showed that pramlintide reduced food intake by 25% in the period of 0-24 hours (it did not cause reduced food intake after 24 hours). But the dosage was substantial – 1000 nmol/kg.
On the other hand, cagrilintide was able to reduce food intake by approximately 50% with a minimal dosage of only 3 nmol/kg. More importantly, this food intake reduction spanned across 60 hours from the moment it was injected.
These results clearly show the potency of cagrilintide in weight loss and diabetes management medication, especially because it acts over such a long time period (allowing subcutaneous injections to be applied once a week).
Reference:
Dehestani B, Stratford NR, le Roux CW. Amylin as a Future Obesity Treatment. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021 Dec 30;30(4):320-325. doi: 10.7570/jomes21071. PMID: 34929674; PMCID: PMC8735818.
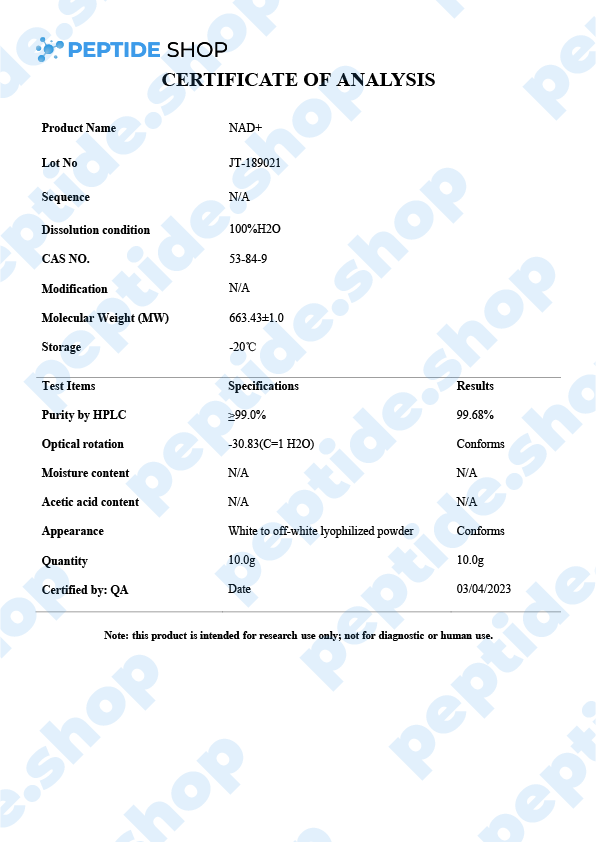
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a critical coenzyme that’s present in every living cell and, as such, is involved in a number of metabolic and cellular processes. This is why NAD+ is so interesting for many different areas of research such as:
- Anti aging
- Metabolic disorders
- Neurodegenerative disorders
- And even cancer research
PeptideShop.com sells NAD+ peptide in vials of 100mg and is meant for laboratory use only. Researchers commonly use it to test its effectiveness on:
- DNA damage repair and gene expression
- Stress response regulation
- Slowing down the progression of degenerative disorders
- Metabolism pathway testing
But, as previously mentioned, we are still waiting on large scale human tests.
NAD+ Role In Cellular Maintenance
Cellular NAD exists in two forms:
- NAD+
- NADH
When there’s a shift in NAD+ and its level drops in favor of NADH, this is a hallmark of aging; though the exact mechanisms that lead to this drop still remain unknown.
Naturally, numerous clinical studies showed that increasing NAD+ levels leads to the reduction of age-related immune and metabolic changes. Meaning there is potential of using NAD+ in treating age related disorders.
NAD+ And Neurodegenerative Disorders
When speaking about aging, one of the most contributing factors is mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons. Aging also speeds up the progression of neurodegenerative disorders, triggering DNA damage and mitochondrial impairment.
Luckily, studies have shown that NAD+ treatment (and even supplementation) helped restore mitochondrial function, enhance neural function and even improve cognitive abilities.
NAD+ And Metabolic Disorders
We’ve seen a dramatic increase in metabolic disorders lately, making it one of the major global health problems. Of course, we use the term metabolic disorders to cluster a whole host of problems such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, as well as some cardiovascular pathologies.
NAD+ levels directly influence nutrient status in cells, so regulating them stands as a clear guideline to future research in hope of making NAD+ an FDA-approved way of treating metabolic and age related disorders.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7973386/

 Anti Aging
Anti Aging Hair Growth
Hair Growth Muscle Growth
Muscle Growth Peptide Blends
Peptide Blends Peptide Supplies
Peptide Supplies Peptides
Peptides Skin
Skin Testosterone
Testosterone Weight Loss
Weight Loss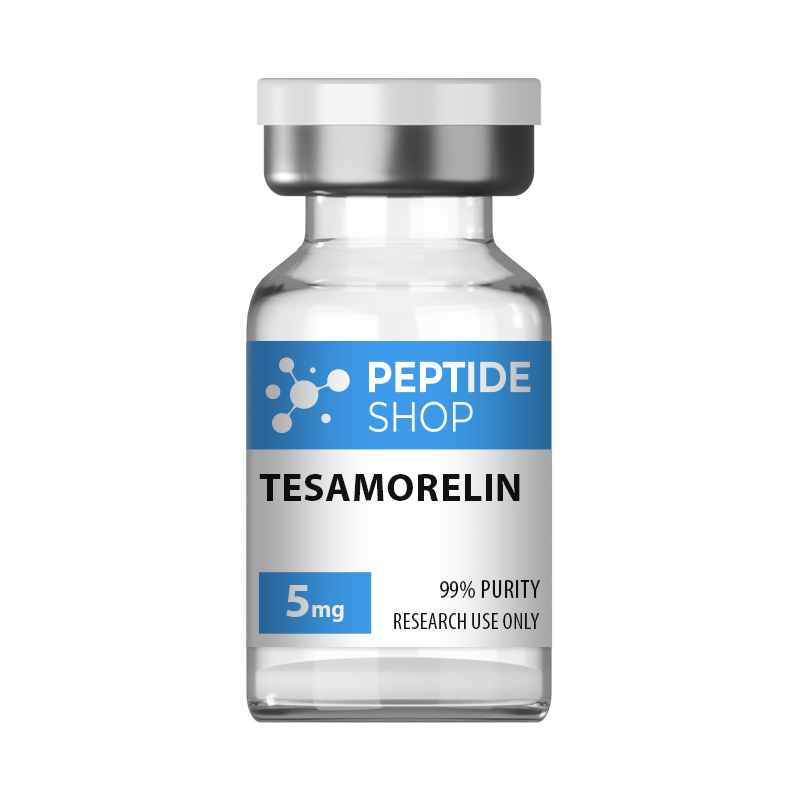










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.